
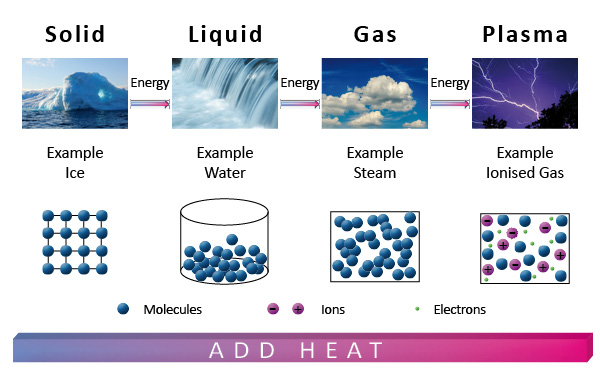
In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist. All physical bodies in the universe are made of matter: galaxies, stars and planets, rocks, water and air. Living organisms like plants, animals and humans are also composed of matter. Since, living organisms are made up of cells. Cells are composed of molecules, which are sets of atoms bonded together. Each atom, in turn, is an assemblage of elementary particles. There are four common states of matter (or phases) in the universe which are observable in our everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma.
- Solids
Solids are material objects in which the constituent particles (ions, atoms, or molecules) are closely packed together in a regularly ordered, repeated pattern. The forces between these particles are provided by either metallic, covalent or ionic bonds that are so strong that the particles cannot move freely but can only vibrate. As a result, a solid has a stable, definite shape, and a definite volume. Solids are generally denser than the other states of matter. Solids also tend to be strong enough to hold their own shape. So they can only change their shape by an outside force, as when broken or cut.
Solids can be transformed into liquids by melting, and liquids can be transformed into solids by freezing. Solids can also change directly into gases through the process of sublimation, and gases can likewise change directly into solids through deposition.
- Liquids

A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. In a liquid, molecules are attracted to each other inter-molecular (or inter-atomic or inter-ionic) forces strongly enough to keep them in contact, but not strongly enough to hold a particular structure. The molecules have enough energy that can continually move with respect to each other and the structure is mobile. This means that liquids can flow smoothly, but not as smoothly as gases. Liquids will tend to take the shape of a container that they are in. This means that the shape of a liquid is not definite but is determined by its container. Liquids are generally less dense than solids, but denser than gases.
Liquids can be transformed into gases by vaporization, and gases can be transformed into solids by condensation. Liquids can also change directly into solids through the process of freezing, and solids can likewise change directly into liquids through melting.
- Gases

Gases are amounts of matter where the molecules have enough kinetic energy so that the effect of inter-molecular forces is small, so that the distance between neighboring molecules are much greater than their molecular size. Hence, the molecules move freely and are independent of each other. Gas is a collection of independent, unbounded molecules which interact mainly by collision. Gases do not exhibit a proper surface, they tend to expand to occupy the whole volume available. A gas is a compressible fluid that has no definite shape or volume, but occupies the entire container in which it is confined.
Gases can be converted into liquid by the process of condensation and the liquids can be converted into gases by vaporization process. Gases can be directly converted into solids by deposition process whereas the solids can be converted directly back into gases by the sublimation process.
- Plasma
Plasma is one of the four fundamental states of matter that are made of ionized matter. The particles in a plasma are a mixture between a liquid and a gas. The particles are free to move, like a liquid, and the attraction is weak, like a gas and was first described by chemist Irving Langmuir in the 1920s. Plasmas are gases that have so much energy that electrons of an atom cannot stay in orbit around one atomic nucleus. The atomic ions and free electrons mix around like a hot soup. Because the positive and negative charged particles are not stuck together, plasma is a good conductor of electricity. It consists of a gas of free electrons and ions (atoms which have some of their orbital electrons removed).

Like a gas, plasma does not have definite shape or volume. Unlike gases, plasmas are electrically conductive, produce magnetic fields and electric currents, and respond strongly to electromagnetic forces.
A gas is usually converted to a plasma in one of two ways, that is, either from a huge voltage difference between two points, or by exposing it to extremely high temperatures. Heating matter to high temperatures causes electrons to leave the atoms, resulting in the presence of free electrons. This creates a so-called partially ionised plasma. At very high temperatures, such as those present in stars, it is assumed that essentially all electrons are "free", and that a very high-energy plasma is essentially bare nuclei swimming in a sea of electrons. This forms the so-called fully ionised plasma.
Examples: the Earth's ionosphere, the Sun's corona, a lightning bolt. Both stars and the interstellar medium are mostly made of plasma. Plasma is the most common state of matter in the universe.

Comments
Post a Comment